Imagine AI as a child growing up. It starts simple, learns to remember, begins to understand others, and eventually—in a distant, theoretical future—gains a sense of self.
As we head towards 2026, the world is obsessed with Artificial Intelligence. But “AI” isn’t just one thing. It’s a spectrum of evolution. To understand where we are going, we need to understand the different “species” of AI that exist today and those dreamed of for tomorrow.
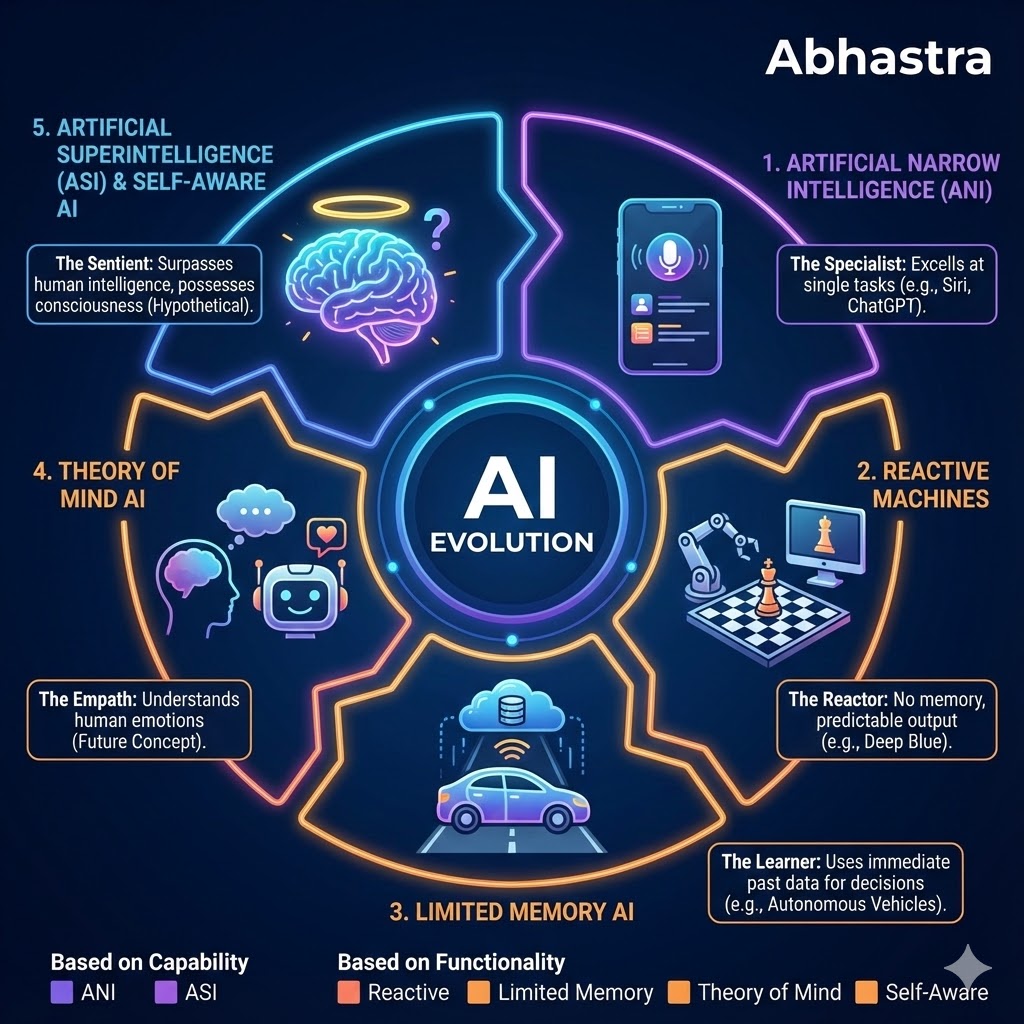
There are generally two ways to classify AI: based on what it can do (Capability) and based on how it works (Functionality).
Here is the story of the five main types of artificial intelligence, from the simplest to the most god-like.
Type 1: The Specialist (Artificial Narrow Intelligence – ANI)
** Classification: Based on Capability**
This is the AI of today. Every single AI you have ever interacted with—from Siri on your phone to the Netflix recommendation engine to ChatGPT—is an Artificial Narrow Intelligence.
ANI is brilliant, but only at one specific thing. A world-champion chess AI cannot write a poem. A self-driving car AI cannot diagnose a disease. They are highly specialized tools, hyper-focused on a single domain. They do not possess genuine understanding; they are just incredibly good at pattern matching within their training data.
- Real-World Examples: Google Search, Tesla Autopilot, Alexa, Spam filters, Generative AI tools like Midjourney.
Type 2: The Reactor (Reactive Machines)
Classification: Based on Functionality
This is the oldest and most basic form of AI. Think of it as an AI with no memory of the past and no concept of the future. It lives entirely in the present moment.
A reactive machine takes an input and provides a predictable output based on pre-programmed rules. It doesn’t learn from its mistakes. The most famous example is IBM’s Deep Blue, the supercomputer that beat chess champion Garry Kasparov in 1997. It could analyze millions of potential moves on the board right now, but it didn’t “remember” the game it played yesterday to improve its strategy.
- Real-World Examples: Deep Blue, basic recommendation engines that only use your current session data.
Type 3: The Learner (Limited Memory AI)
Classification: Based on Functionality
This is the next step in evolution. Limited Memory AI can look into the immediate past to make better decisions in the present.
Almost all modern AI applications, including Generative AI and self-driving cars, fall into this category. A self-driving car doesn’t just see the road right now; it remembers the speed and trajectory of other cars from a few seconds ago to predict where they will be next. Large Language Models (LLMs) like ChatGPT “remember” the earlier parts of your conversation to provide context-aware answers. However, their “memory” is limited to a short window or training dataset; they don’t have a lifelong, accumulating experience like a human.
- Real-World Examples: Self-driving vehicles, chatbots like ChatGPT and Gemini, virtual assistants.
Type 4: The Empath (Theory of Mind AI)
Classification: Based on Functionality
Now we enter the realm of the future. This type of AI does not exist yet.
“Theory of Mind” is a psychological term for the ability to understand that other beings have their own thoughts, emotions, beliefs, and intentions that impact their behavior. A Theory of Mind AI wouldn’t just process your commands; it would understand why you are asking, gauge your emotional state, and adjust its behavior accordingly. It would be a true social companion, capable of empathy and complex social negotiation.
- Future Concept: An AI therapist that can read subtle emotional cues or a customer service bot that truly understands your frustration.
Type 5: The Sentient (Artificial Superintelligence – ASI & Self-Aware AI)
Classification: Based on Capability & Functionality
This is the final frontier, the stuff of science fiction movies like Her or Ex Machina.
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) is the hypothetical point where an AI becomes as smart as a human across all domains—it can learn, reason, plan, and create just like us.
Artificial Superintelligence (ASI) is what happens next: an intelligence that far surpasses the brightest human minds in practically every field, including scientific creativity, general wisdom, and social skills.
A Self-Aware AI is the functional equivalent: a machine that not only thinks but has consciousness. It knows it exists, has its own feelings, needs, and beliefs. This level of AI raises profound ethical questions and remains a distant, debated possibility.
- Future Concept: A superintelligent system that solves climate change or cures all diseases—or a sentient machine that demands its own rights.